Optionals types in Swift either have a value or not, and there are several ways to test optionals using the XCTest framework. APIs like XCTUnwrap are designed to unwrap an optional and throw an error if unwrapping failed. However, it can easily lead to writing many unwraps before evaluating the actual outcome you want to test for.
If you’re new to unit testing or just a bit inexperienced, you might first want to read my article on unit test best practices. I also encourage you to read about testing private methods and variables, as this will bring you up to speed on the basics of unit testings. This post will go over using XCTUnwrap vs. writing a custom convenience method for testing optionals. New to optionals? You can read everything about them in my article Optionals in Swift explained: 5 things you should know.
Using XCTUnwrap to unwrap optionals
XCTUnwrap is a method available in the XCTest framework for unwrapping optionals in unit tests. Whenever an unwrap fails because of a missing value, it will throw an error and fail the unit test. An example looks as follows:
func testOptional() throws {
let optionalValue: Int? = 10
let unwrappedValue = try XCTUnwrap(optionalValue)
XCTAssertEqual(unwrappedValue, 10)
}In this example, the optional value is set to 10 and will result in a succeeding test. However, if the optional value were to be nil, the unit test would fail with a describing message:

XCTUnwrap is great if you want to fail a test early if a value does not exist. We could’ve skipped the unwrapping by directly matching the optional value:
func testOptionalWithoutUnwrap() throws {
let optionalValue: Int? = nil
XCTAssertEqual(optionalValue, 10)
}This works great if you only have to assert one value. However, if you were to assert for properties on an optional instance, you could end up with multiple failing assertions just because the instance is nil:

In that case, it’s better first to unwrap your instance using XCTUnwrap and continue evaluation if you know the person instance exists:
func testPersonValues() throws {
let optionalPerson: Person? = nil
let unwrappedPerson = try XCTUnwrap(optionalPerson)
XCTAssertEqual(unwrappedPerson.name, "Antoine")
XCTAssertEqual(unwrappedPerson.age, 30)
}In this case, the unit test will directly fail as soon as it encounters a nil value for the person instance.
Creating custom assertion methods to test with optionals
Another problem we often run into when testing optionals is that XCTAssertTrue or XCTAssertFalse doesn’t work with optionals:
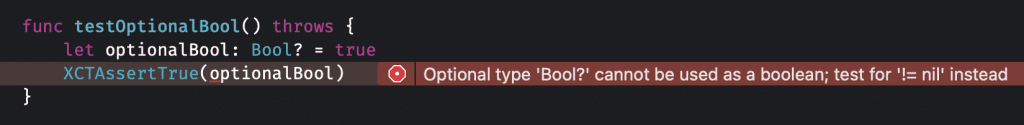
The suggestion makes it even worse, as checking for != nil does not mean the boolean value is true.
A common solution is to write one of the following assertions:
XCTAssertTrue(optionalBool == true)
XCTAssert(optionalBool == true) The first one has a duplicate true statement, while the second one is less describing in its name.
Creating global overloads for standard assert methods
As a solution, we can write our own global method overloads to handle optional assertion matching:
/// Allows asserting for optionals to be `true`.
/// - Parameters:
/// - expression: The expression to assert on.
/// - message: An optional message to throw once comparing fails.
/// - file: The file in which the assertion takes place.
/// - line: The line on which the assertion takes place.
public func XCTAssertTrue(_ expression: @autoclosure () throws -> Bool?, _ message: @autoclosure () -> String = "", file: StaticString = #file, line: UInt = #line) {
guard let value = try? expression() else {
XCTFail("Unwrapping of expected boolean failed", file: file, line: line)
return
}
XCTAssertTrue(value as Bool, message(), file: file, line: line)
}
/// Allows asserting for optionals to be `false`.
/// - Parameters:
/// - expression: The expression to assert on.
/// - message: An optional message to throw once comparing fails.
/// - file: The file in which the assertion takes place.
/// - line: The line on which the assertion takes place.
public func XCTAssertFalse(_ expression: @autoclosure () throws -> Bool?, _ message: @autoclosure () -> String = "", file: StaticString = #file, line: UInt = #line) {
guard let value = try? expression() else {
XCTFail("Unwrapping of expected boolean failed", file: file, line: line)
return
}
XCTAssertFalse(value as Bool, message(), file: file, line: line)
} This is great as it allows us to write the unit tests from before as follows:
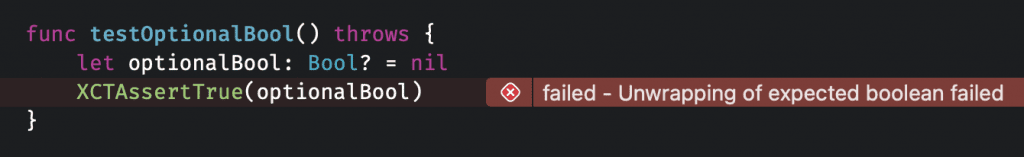
This improves the readability of our code and results in a describing failure message as soon as unwrapping failed.
Conclusion
There are many ways of testing optionals using the standard XCTest APIs, but they don’t always result in the most readable code. By writing convenience overloads, we can use the standard XCTAssertTrue and XCTAssertFalse using optionals and write readable unit tests.
If you like to improve your Swift knowledge, even more, check out the Swift category page. Feel free to contact me or tweet to me on Twitter if you have any additional tips or feedback.
Thanks!